objects Literal :- You Just Literaly Open And Close a curly braces and write properties and methods
Factory Function: you Create a function and inside the function retun the object literal , and to call it declar a variable and call the function
constructor Function: You create a function and use this to assign properties and methods and use new keyword along with function name to create an instance of the constructor; (Constructor Functions Start With An Upper case letter)
Functions Are Objects :-
note ["every object in js has an constructor property"]
note ["When We Create a function using This Syntax [ function circle(){}"] internaly Function constructor runs and create the function ]
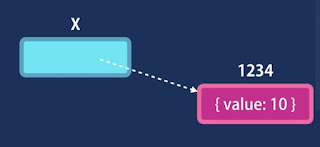
values :- copies Value
reference :- copies reference
Adding and deleting Properties :- you can add a property by just writeing the Instance name Either . Or [] And Then Add Like Object literal
to delete write delete in front of the objcet
Enumearting properties: You can Enumearte over properties by a for loop like
function Circle(radies){
this.radies = radies;
this.draw = function() {
console.log('draw');
}
}
const circle = new Circle(10);
for (let key in circle){
console.log(key, circle[key]);
}
Objcet.keys(circle); / It Returens all the keys in the circle object as an array;
check the existance of a property or method in an object use
in
example
if ('radies' in circle){
// do something
}
Abstraction
in javascript we use let to declar private variable if we have a function and inside it we have properties and methods that we wanted to make private we must make them local varibale or local function using let
clousers in javascript
in clousers we preserve the local variable and function if they are user in any child function of that function
Getters And Setters
the Problem with Setting private variable and function is that You cant access Them in other places
but if you want yo show them then either use this.getFunctionName = () =>{
return the variable;
};
or you can use Objcet.defineProperties() to set up getters and setters
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
In Javascript we do not have classes we have objects thats why in js we use prototypical inheritance
prototype is just an object it self but prototype is just parent in js a object inherits from its parent
every object In js has a perent its '__proto__' or prototype just __proto__ dont have __proto__
prototypical inheritance :- if we use a method in our javascript objcet but dont define it javascript engine check to its parent all the waty to '__proto__' ;
Multilevel inheritance :-
in js when we declar an empty array what happends is its get inherited from arraybase or prototype and create an array but the prototype is it self an object and get inherited from __proto__ or prototype its an example of multilevel inheritance
Note** all object created by the object constructor would have the same prototype
Property Descriptors
constructor Properties
you can get the prototype by either myobj.__proto__ or Objcet.getPrototypeOf(myobj)
it retun the all the prototypes in this objcet
in javascript function are also objcets
prototypes Properties and method vs instance Properties and method
take method from instance members and put it into objcet base
function Circle(){
this.draw()= () =>{
something
}
};
to add on objcet base
Circle.prototype.draw=() => {
something
} ;
javascript specificity 101
if you have a method in instance members and properties members javascript is first gona look at the instance members and then go to prototype members
opps In Javascript (Brad Traversy)
prototypical inheritance
.call() => method call allows us to call other function from other places in the current context
inherits the person prototype method
Customer.prototype = Object.create(Person.prototype)
=================================================================
Using Object.create
or we can use js classes (es6)
es6 static method
put static before a function and call using class name
=============================================================
modules in js
split =:> modules
common js
cohesion -> related Data Should be together
by default module is private Explictly export it to expose
and require it to import
ES6 modules
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Ways To define objects in Javascript
1 Object literal
2 factory function
3 constructor way
4 es6 class way
 |
| Object literal |
 |
| factory function |
 |
| constructor Way |
Function() { prototype }
Value Type Vs Reference Type
primitive types objects
null array (also objects)
undefined function (also objects)





No comments:
Post a Comment